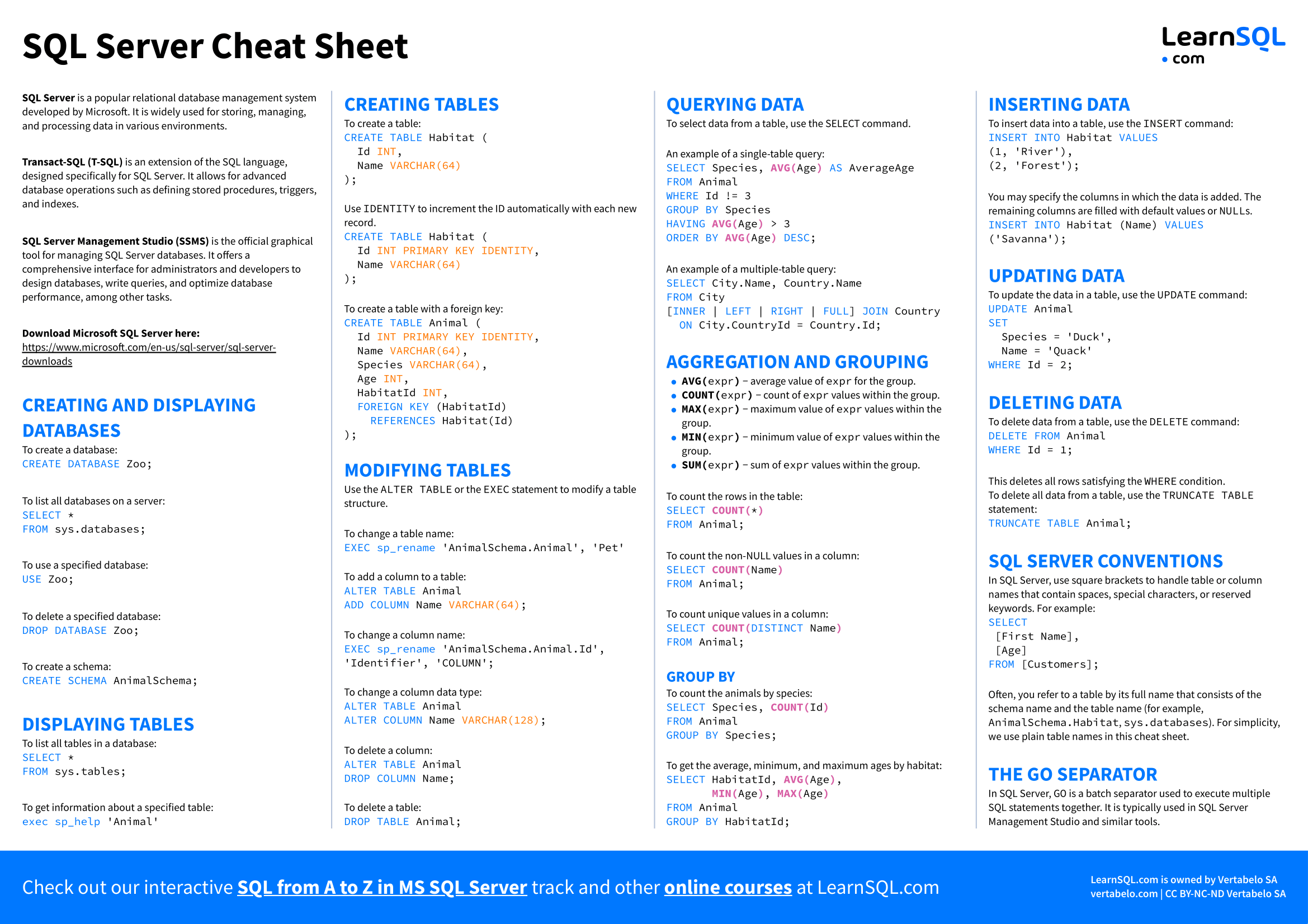
This cheat sheet is a comprehensive guide to SQL Server, offering a quick reference to its essential commands. It covers the basics of creating and displaying databases and tables, the commands to modify tables, and the fundamental syntax for T-SQL commands such as SELECT , INSERT , UPDATE , and DELETE . Additionally, it delves into the most common text and numeric functions, as well as functions that handle NULL values. For those working with date and time data, the cheat sheet provides insights into the relevant data types, functions, and common patterns.
Download Options:
For visual enthusiasts:
If you prefer a more visual approach or need a digital-friendly version for various applications, we also offer the cheat sheet as a high-resolution PNG image. To download, right-click (for desktop users) or long tap (for mobile users) on the image.

SQL Server is a popular relational database management system developed by Microsoft. It is widely used for storing, managing, and processing data in various environments.
Transact-SQL (T-SQL) is an extension of the SQL language, designed specifically for SQL Server. It allows for advanced database operations such as defining stored procedures, triggers, and indexes.
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is the official graphical tool for managing SQL Server databases. It offers a comprehensive interface for administrators and developers to design databases, write queries, and optimize database performance, among other tasks.
Download Microsoft SQL Server here:
Complete learning path for SQL Server. Try out our SQL from A to Z in MS SQL Server track. 7 hands-on T-SQL courses with over 800 exercises!
To create a database:
CREATE DATABASE Zoo;
To list all databases on a server:
SELECT *FROM sys.databases;
To use a specified database:
USE Zoo;
To delete a specified database:
DROP DATABASE Zoo;
To create a schema:
CREATE SCHEMA AnimalSchema;
To list all tables in a database:
SELECT *FROM sys.tables;
To get information about a specified table:
exec sp_help 'Animal'
To create a table:
CREATE TABLE Habitat ( IdINT , NameVARCHAR(64) );
Use IDENTITY to increment the ID automatically with each new record.
CREATE TABLE Habitat ( IdINT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY , NameVARCHAR(64) );
To create a table with a foreign key:
CREATE TABLE Animal ( IdINT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY , NameVARCHAR(64) , SpeciesVARCHAR(64) , AgeINT , HabitatIdINT ,FOREIGN KEY (HabitatId)REFERENCES Habitat(Id) );
Use the ALTER TABLE or the EXEC statement to modify a table structure.
To change a table name:
EXEC sp_rename 'AnimalSchema.Animal', 'Pet'
To add a column to a table:
ALTER TABLE AnimalADD COLUMN NameVARCHAR(64) ;
To change a column name:
EXEC sp_rename 'AnimalSchema.Animal.Id', 'Identifier', 'COLUMN';
To change a column data type:
ALTER TABLE AnimalALTER COLUMN NameVARCHAR(128) ;
To delete a column:
ALTER TABLE AnimalDROP COLUMN Name;
To delete a table:
DROP TABLE Animal;
To select data from a table, use the SELECT command.
An example of a single-table query:
SELECT Species,AVG( Age) AS AverageAgeFROM AnimalWHERE Id != 3GROUP BY SpeciesHAVING AVG( Age) > 3ORDER BY AVG( Age) DESC ;
An example of a multiple-table query:
SELECT City.Name, Country.NameFROM City [INNER |LEFT |RIGHT |FULL ]JOIN CountryON City.CountryId = Country.Id;
Learn T-SQL by actually writing code. Complete 130 interactive exercises in our SQL Basics in MS SQL Server course and gain confidence in your coding skills.
To count the rows in the table:
SELECT COUNT( *) FROM Animal;
To count the non-NULL values in a column:
SELECT COUNT( Name) FROM Animal;
To count unique values in a column:
SELECT COUNT( DISTINCT Name) FROM Animal;
To count the animals by species:
SELECT Species,COUNT( Id) FROM AnimalGROUP BY Species;
To get the average, minimum, and maximum ages by habitat:
SELECT HabitatId,AVG( Age) ,MIN( Age) ,MAX( Age) FROM AnimalGROUP BY HabitatId;
To insert data into a table, use the INSERT command:
INSERT INTO HabitatVALUES (1, 'River'), (2, 'Forest');
You may specify the columns in which the data is added. The remaining columns are filled with default values or NULL s.
INSERT INTO Habitat (Name)VALUES ('Savanna');
To update the data in a table, use the UPDATE command:
UPDATE AnimalSET Species = 'Duck', Name = 'Quack'WHERE data
To delete data from a table, use the DELETE command:
DELETE FROM AnimalWHERE >This deletes all rows satisfying the WHERE condition.
To delete all data from a table, use the TRUNCATE TABLE statement:
TRUNCATE TABLE Animal;
In SQL Server, use square brackets to handle table or column names that contain spaces, special characters, or reserved keywords. For example:
SELECT [First Name], [Age]FROM [Customers];
Often, you refer to a table by its full name that consists of the schema name and the table name (for example, AnimalSchema.Habitat , sys.databases ). For simplicity, we use plain table names in this cheat sheet.
In SQL Server, GO is a batch separator used to execute multiple SQL statements together. It is typically used in SQL Server Management Studio and similar tools.
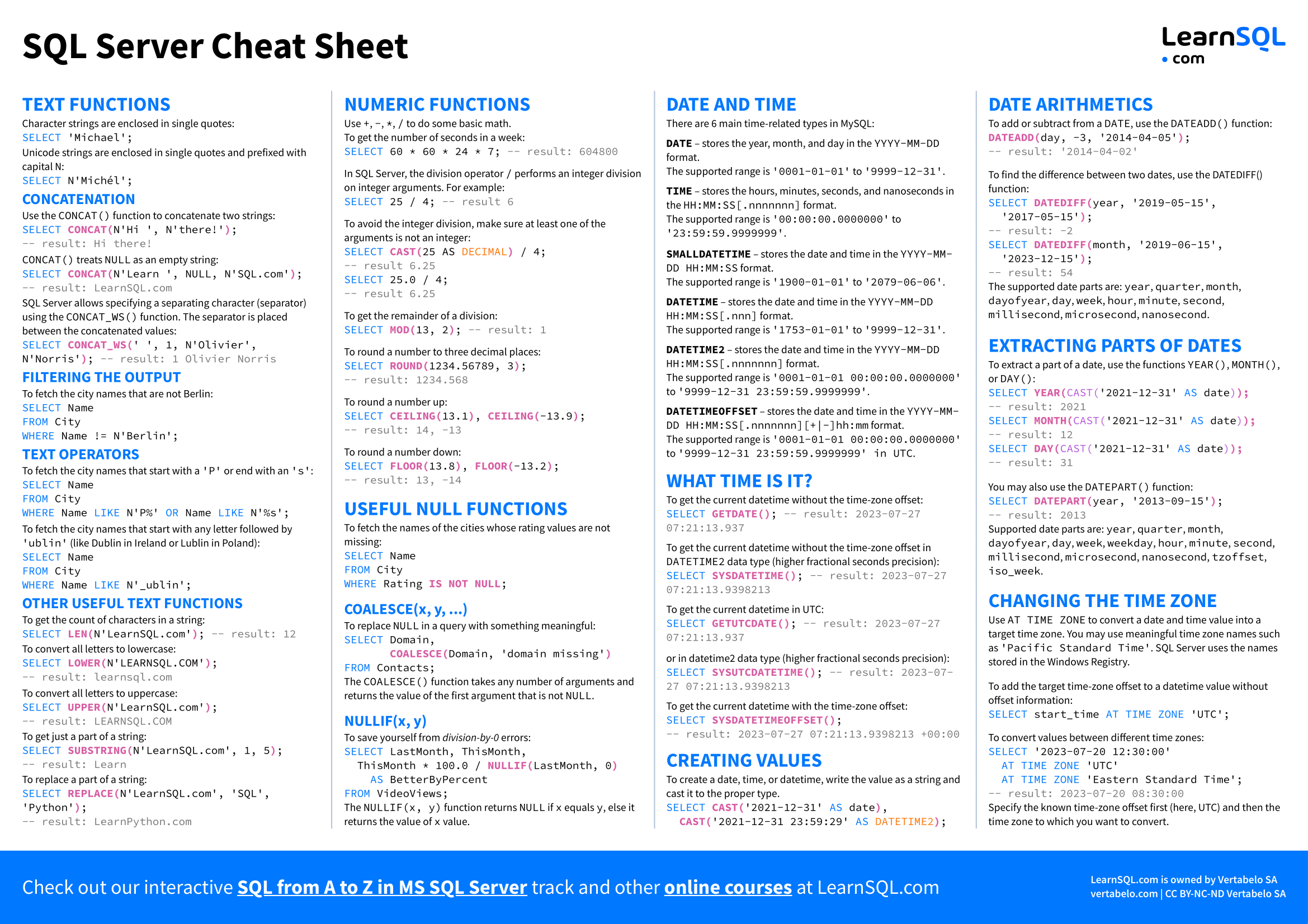
Character strings are enclosed in single quotes:
SELECT 'Michael';
Unicode strings are enclosed in single quotes and prefixed with capital N :
SELECT N'Michél';
Use the CONCAT() function to concatenate two strings:
SELECT CONCAT( N'Hi ', N'there!') ;-- result: Hi there!
CONCAT() treats NULL as an empty string:
SELECT CONCAT( N'Great ', N'day', NULL) ;-- result: Great day
SQL Server allows specifying a separating character (separator) using the CONCAT_WS() function. The separator is placed between the concatenated values:
SELECT CONCAT_WS( ' ', 1, N'Olivier', N'Norris') ;-- result: 1 Olivier Norris
To fetch the city names that are not Berlin:
SELECT NameFROM CityWHERE Name != N'Berlin';
To fetch the city names that start with a 'P' or end with an 's' :
SELECT NameFROM CityWHERE NameLIKE N'P%'OR NameLIKE N'%s';
To fetch the city names that start with any letter followed by 'ublin' (like Dublin in Ireland or Lublin in Poland):
SELECT NameFROM CityWHERE NameLIKE N'_ublin';
To get the count of characters in a string:
SELECT LEN( N'LearnSQL.com') ;-- result: 12
To convert all letters to lowercase:
SELECT LOWER( N'LEARNSQL.COM') ;-- result: learnsql.com
To convert all letters to uppercase:
SELECT UPPER( N'LearnSQL.com') ;-- result: LEARNSQL.COM
To get just a part of a string:
SELECT SUBSTRING( N'LearnSQL.com', 1, 5) ;-- result: Learn
To replace a part of a string:
SELECT REPLACE( N'LearnSQL.com', 'SQL', 'Python') ;-- result: LearnPython.com
The best place to master SQL Server functions is our Common Functions in MS SQL Server interactive course.
Use + , - , * , / to do some basic math.
To get the number of seconds in a week:
SELECT 60 * 60 * 24 * 7;-- result: 604800
In SQL Server, the division operator / performs an integer division on integer arguments. For example:
SELECT 25 / 4;-- result 6
To avoid the integer division, make sure at least one of the arguments is not an integer:
SELECT CAST( 25 ASDECIMAL ) / 4;-- result 6.25 SELECT 25.0 / 4;-- result 6.25
To get the remainder of a division:
SELECT MOD( 13, 2) ;-- result: 1
To round a number to three decimal places:
SELECT ROUND( 1234.56789, 3) ;-- result: 1234.568
To round a number up:
SELECT CEILING( 13.1) ,CEILING( -13.9) ;-- result: 14, -13
To round the number down:
SELECT FLOOR( 13.8) ,FLOOR( -13.2) ;-- result: 13, -14
To fetch the names of the cities whose rating values are not missing:
SELECT NameFROM CityWHERE RatingIS NOT NULL ;
To replace NULL in a query with something meaningful:
SELECT Domain,COALESCE( Domain, 'domain missing') FROM Contacts;
The COALESCE() function takes any number of arguments and returns the value of the first argument that is not NULL .
To save yourself from division-by-0 errors:
SELECT LastMonth, ThisMonth, ThisMonth * 100.0 /NULLIF( LastMonth, 0) AS BetterByPercentFROM VideoViews;
The NULLIF(x, y) function returns NULL if x equals y , else it returns the value of x value.
There are 6 main time-related types in MySQL:
To get the current datetime without the time-zone offset:
SELECT GETDATE() ;-- result: 2023-07-27 07:21:13.937
To get the current datetime without the time-zone offset in DATETIME2 data type (higher fractional seconds precision):
SELECT SYSDATETIME() ;-- result: 2023-07-27 07:21:13.9398213
To get the current datetime in UTC:
SELECT GETUTCDATE() ;-- result: 2023-07-27 07:21:13.937
or in datetime2 data type (higher fractional seconds precision):
SELECT SYSUTCDATETIME() ;-- result: 2023-07-27 07:21:13.9398213
To get the current datetime with the time-zone offset:
SELECT SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() ;-- result: 2023-07-27 07:21:13.9398213 +00:00
To create a date, time, or datetime, write the value as a string and cast it to the proper type.
SELECT CAST( '2021-12-31'AS date) ,CAST( '2021-12-31 23:59:29'AS DATETIME2 ) ;
The best place to master SQL Server functions is our Common Functions in MS SQL Server interactive course.
To add or subtract from a DATE , use the DATEADD() function:
SELECT DATEADD( day, -3, '2014-04-05') ;-- result: '2014-04-02'
To find the difference between two dates, use the DATEDIFF() function:
SELECT DATEDIFF( year, '2019-05-15', '2017-05-15') ;-- result: -2 SELECT DATEDIFF( month, '2019-06-15', '2023-12-15') ;-- result: 54
The supported date parts are: year , quarter , month , dayofyear , day , week , hour , minute , second , millisecond , microsecond , nanosecond .
To extract a part of a date, use the functions YEAR() , MONTH() , or DAY() :
SELECT YEAR( CAST( '2021-12-31'AS date) ); -- result: 2021
SELECT MONTH( CAST( '2021-12-31'AS date) ); -- result: 12
SELECT DAY( CAST( '2021-12-31'AS date) ); -- result: 31
You may also use the DATEPART() function:
SELECT DATEPART( year, '2013-09-15') ;-- result: 2013
Supported date parts are: year , quarter , month , dayofyear , day , week , weekday , hour , minute , second , millisecond , microsecond , nanosecond , tzoffset , iso_week .
Use AT TIME ZONE to convert a date and time value into a target time zone. You may use meaningful time zone names such as 'Pacific Standard Time' . SQL Server uses the names stored in the Windows Registry.
To add the target time-zone offset to a datetime value without offset information:
SELECT start_timeAT TIME ZONE 'UTC';
To convert values between different time zones:
SELECT '2023-07-20 12:30:00'AT TIME ZONE 'UTC'AT TIME ZONE 'Eastern Standard Time';-- result: 2023-07-20 08:30:00
Specify the known time-zone offset first (here, UTC) and then the time zone to which you want to convert.