
Learn about the essential Heart Attack Test, its procedure, and its significance in identifying cardiac health concerns for proactive care.

By Bernard Ramirez on Jul 17, 2024.
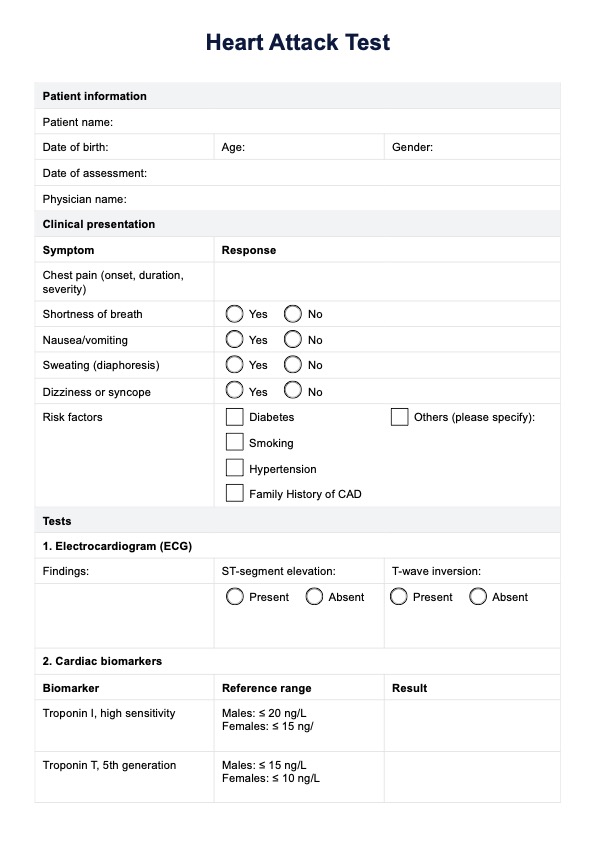

A heart attack test is an examination or series of assessments to detect indicators or risk factors associated with a potential heart attack. These tests are pivotal in evaluating heart health, aiding in early identification, and minimizing the risk of cardiac incidents.
Numerous tests can determine the likelihood of a heart attack or assess the current state of cardiovascular health. These may include blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECG or EKG), echocardiograms, stress test, cardiac catheterization, and advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans. Each test identifies explicitly irregularities in the heart's structure, function, or blood supply.
Blood tests are fundamental, measuring certain enzymes and proteins that leak into the blood after heart damage. ECGs monitor the heart's electrical activity, detecting irregular rhythms or signs of a prior heart attack. Additionally, echocardiograms use sound waves to produce images, offering insights into the heart's structure and functioning. Stress tests evaluate heart performance during physical activity, and cardiac catheterization provides detailed images of blood vessels around the heart.
These tests collectively contribute to a comprehensive understanding of an individual's heart health, enabling healthcare providers to diagnose potential concerns, determine appropriate treatments, and implement preventive measures. Regular screenings are crucial, especially for individuals with risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease.
Understanding and conducting these tests are pivotal in promoting cardiovascular health, allowing for early intervention and lifestyle modifications that can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks and other cardiac issues.